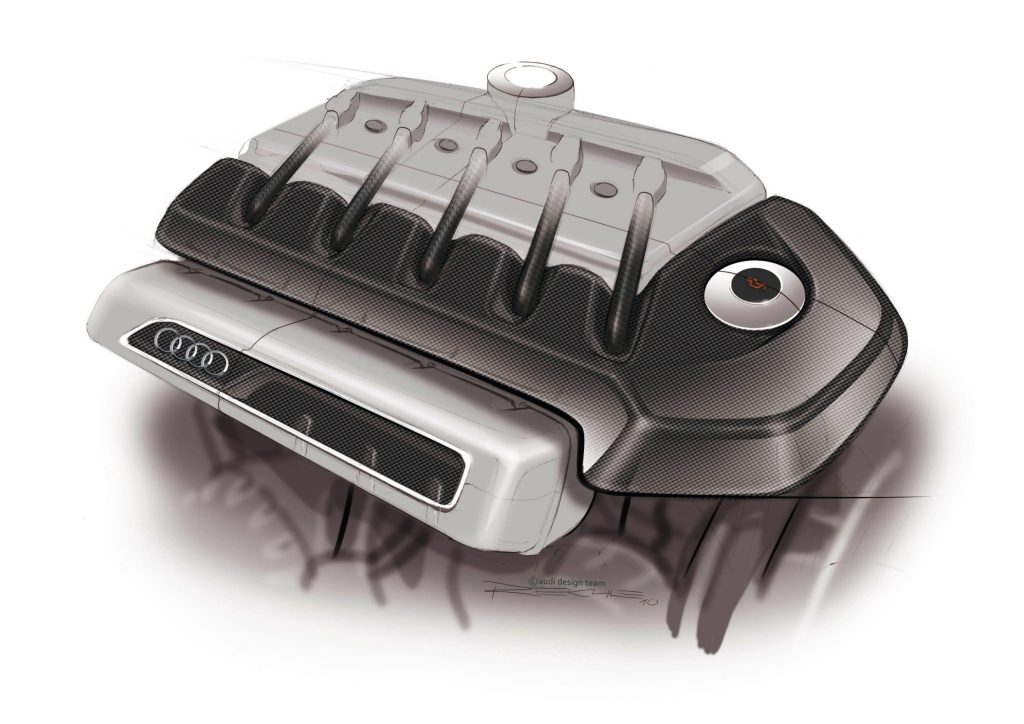

1-2-4-5-3: The Return of a Unique Concept
“At the time we said to ourselves: the TT is a real sports car, and a high-performance version of it simply belongs on the road.”
— Stephan Reil, former Head of Technical Development at quattro GmbH
[source: Audi AG]
After two RS 4 and RS 6 models, each in the mid-range, quattro GmbH presented its first compact class vehicle in 2009: the Audi TT RS. “We said to ourselves at the time: The TT is a real sports car, and a high-performance version of it simply belongs on the road,” says Stephan Reil, then Chief Developer at quattro GmbH. First of all, a suitable engine to base the pioneering project on had to be found. An engine that offers sufficient scope for increasing the performance of the second-generation TT to match those of high-performance RS models. Stephan Reil found it in an Audi concept that achieved cult status from 1976 to 1997 and not least in the original quattro of 1980: the five-cylinder engine.
Such an in-line engine with the unique 1-2-4-5-3 ignition sequence and the unmistakable sound associated with it has not been in Audi’s range for almost twelve years, but its sister brand Volkswagen did have it in its line-up. Based on the 2.5-liter five-cylinder engine from the U.S. version of the VW Jetta with the internal identifier EA 855, quattro GmbH developed a high-performance unit: A reinforced engine block with a modified cylinder head and gasoline direct injection TFSI together with a turbocharger for high efficiency and low emissions.

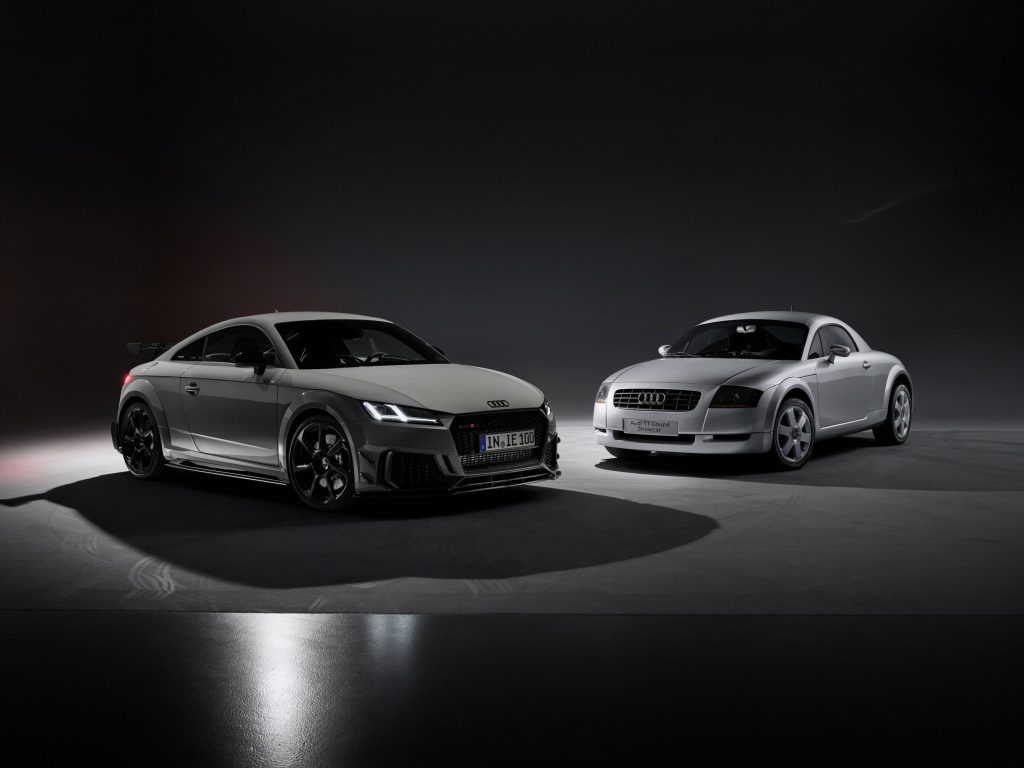
The relaunch of the five-cylinder concept gave the first Audi TT RS an output of 250 kW (340 hp). Unlike its predecessors in the larger Audi models, the inline five-cylinder engine of this second generation did fit longitudinally, but only when transversely installed in the more compact dimensions of the TT’s front end. Subsequently, the 2.5-liter turbo five-cylinder developed into another globally celebrated Audi trademark. The continuously improved power unit was named “International Engine of the Year” nine times in succession.
Unlike the RS 4 and RS 6 models, the quattro drivetrain system, which is mandatory for RS models, does not distribute the engine power to the four wheels via a Torsen center differential in the Audi TT RS. Instead, for the first time in a quattro GmbH vehicle, it uses the Haldex principle. This means that in addition to the drive shafts of the front wheels, an angular drivetrain in the transmission transmits the driven forces toward the rear axle. The first Audi TT RS and its successors are offered as a coupe and roadster.
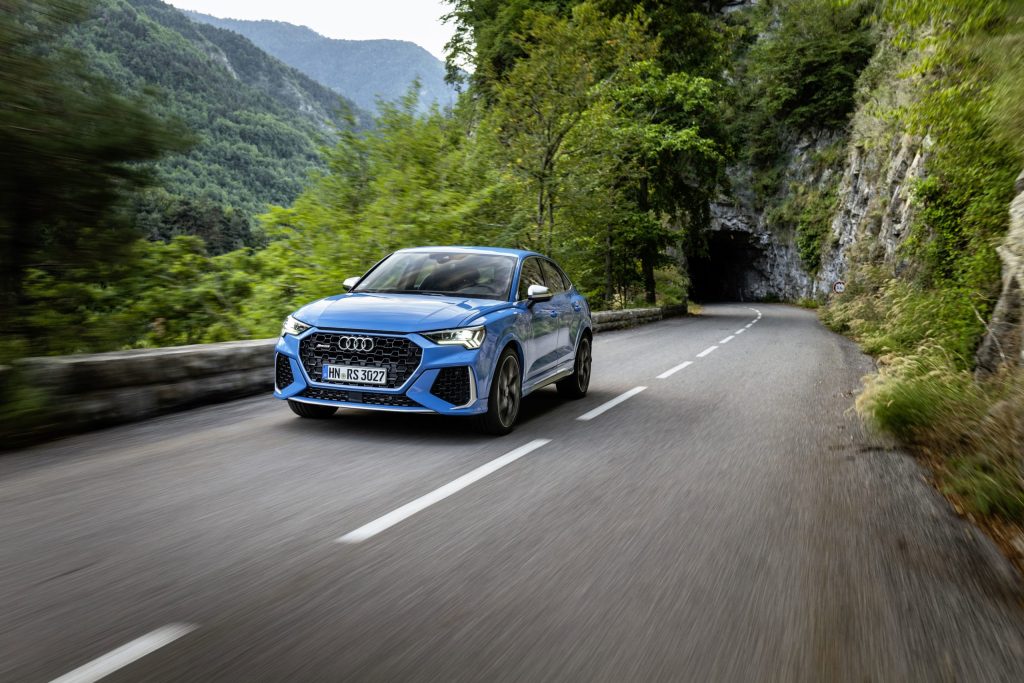
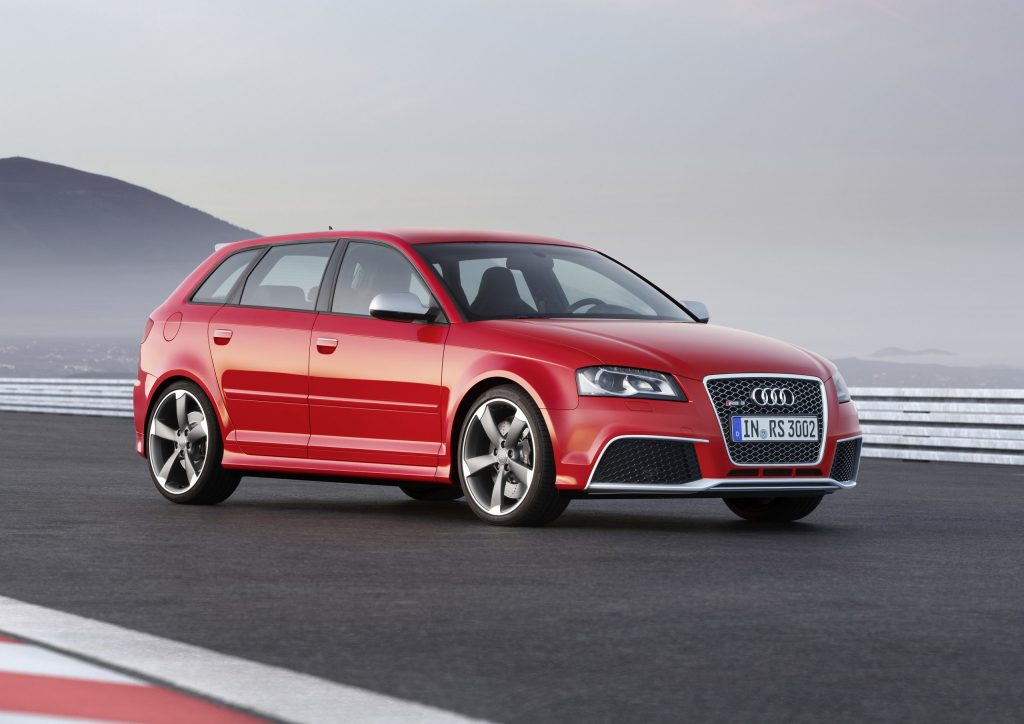
Audi Sport GmbH (named quattro GmbH until 2016) continues its successful five-cylinder tradition to this day in the models from the A-segment, in addition to the TT RS, i.e. in both the RS 3 and the RS Q3. The latest version of the 2.5-liter TFSI turbocharged engine, the most powerful to date at 299 kW (407 hp), operates in the performance edition of the Audi RS 3* presented as a sedan and as a Sportback* in 2022. “For me, the five-cylinder is an absolute icon that we continue to perfect to this day. The lap record of our current Audi RS 3 on the Nürburgring-Nordschleife in 2021 impressively demonstrated what the engine is capable of in its highest configuration stage in combination with the torque splitter,” says Steffen Bamberger, Head of Technical Development at Audi Sport GmbH.













Responses